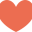
这里描述了IgG的结构,以及它的域和子域。第一部分讨论的是Fc区域,也称为可结晶片段区域。它是抗体的尾部区域和与细胞表面受体相互作用的区域。大多数效应函数是在与这个区域结合后产生的。需要注意的是,Fc包含一个高度保守的n -糖基化位点,这对F-C受体介导的功能非常重要。Fab区也被称为抗原结合区,因为它的名字是抗体与抗原结合的位置,具体称为副位。副位位于可变区,这是抗体对相应抗原特异性高的原因。在Fab区域,还有一个区域叫做CDR区域,它代表互补决定区域。CDR由与抗原相互作用的B或t细胞决定,并决定抗原的表位。一旦接触抗原,b细胞产生抗体CDR地区,都有一个特定的抗原决定基相互作用,也被称为抗体结合部位(如前所述),科学发达的技术发现被允许基因改造小鼠马伯产生嵌合体马伯,让成功的进入了马伯疗法。(Dowling, Chavaillaz et al. 2005)在chimeric看来,mAb现在是小鼠/人类mAb的混合体,它的行为更像一个自然的人类mAb。这一变化使得宿主不太可能将单克隆抗体视为外来抗原,同时也增加了分子的半衰期。反过来,嵌合性允许单克隆抗体产生正常的效应作用,以及与恶性细胞产生适当的相互作用。
英国生物学作业代写 单克隆抗体
Here is described the structure of an IgG, with its domains and subdomains. The first section to talk about is the Fc region, also known as the crystallizable fragment region. It is the tail region of the antibody and the region that interacts with cell surface receptors. Most effector functions are produced after binding with this region. The important thing to note about the Fc is that it contains a highly conserved N-glycosylation site, which is important to FC receptor-mediated function. The Fab region is also known as the antigen-binding region, as in its name this is the location of where the antibody binds to antigens, specifically called the paratope. The paratope is located in the variable domain, which is the reason for the high specificity of the antibody to its corresponding antigen. In the Fab region, there is another region called the CDR region, which stands for complementary determining regions. The CDR is determined by B or T-cells interacting with the antigen and determines the epitope of the antigen. Once interacting with an antigen, the B-cells produce an antibody with a CDR region that has a specific interaction with the epitope, also known as the paratope (as mentioned earlier) As science developed techniques were discovered that allowed genetic modification of murine mAbs to produce chimeric mAbs, that allowed the ushering in of successful mAb therapy. (Dowling, Chavaillaz et al. 2005) By chimeric, the mAb is now a hybrid of mouse/human mAb and behaves more like a natural human mAb. This change allows the host to less likely to view the mAb as a foreign antigen, as well as increasing the half-life of the molecule. In turn, the chimeric nature allows the mAb to induce normal effector functions, as well as induce proper interactions with malignant cells.
本段内容来自网络 并不是我们的写手作品 请勿直接剽窃,查重100%,造成后果与本站无关。如需定制论文请记得联系我们。